avm classification radiology
Bone erosion sclerotic change periosteal reaction and pathologic fracture each suggest bone involvement. Vascular tumors are further classified as benign locally aggressive or malignant.

Pin By Phuong Hoai On Radio Notes Hemorrhage Vascular Mri
Image quality of 4D contrast-enhanced MR angiography was judged to be at least adequate for diagnosis in all patients by both readers.

. Benign infantile hemangiomas represent the vast majority of vascular tumors and occur most commonly in their sporadic form. Spinal arteriovenous malformations can be classified in a number of ways. 1 arterial 2 arteriovenous connection and 3 draining veins.
Conventional radiography plays only a small part in the diagnosis and classification of vascular lesions but it provides useful information about bone and joint involvement. They can occur anywhere in the body but are most common in the brain 1. Although transcatheter embolization is a less-invasive and effective treatment option it has a potential risk of complications including renal.
According to the classification of redekop et al 7 of arterial avm-associated intracranial aneurysms flow-related aneurysms should be considered proximal if they are located on the supraclinoid internal carotid artery the circle of willis the middle cerebral artery up to and including the primary bifurcation the anterior cerebral artery up. 3 This classification has four stages with stage 1 lesions being asymptomatic and stage 4 representing high-output heart failure. Digital substraction angiography DSA is usually performed for guidance during the embolization session but is also essential to properly classify a specific lesion according to its anatomy.
Within the cord parenchyma or subarachnoid space 6. There are several subgroups the most common being glomerular type brain AVMs with fistulous type AVMs being less common. Spinal AVMs may be classified as intramedullary and extramedullary 80 1 and further divided into four angiographic types with additional subtypes 2-3 see.
80 1 Or into four types 2. The most recent classification scheme of 2014 continues to divide vascular anomalies into vascular tumors and vascular malformations. Histopathologically AVMs may be classified as cirsoid or cavernous depending on the number and diameter of the intra-lesional vessels.
Single coiled vessel spinal dural AV fistula type II. Their frequency varies occurring in roughly 10 to 20 persons per 100000. Hemangioma and arteriovenous malformation AVM are the most commonly used terms and are the mostly incorrectly used as well.
Phleboliths are specific to hemangioma. 34 they are classified according to the hamburg classification 35 as truncular or extratruncular with 40 of lesions localized to the extremities 20 on the trunk and 40 on the head and neck. We believe this generalization to be improper because 1 the classification does not assess the special characteristics of an avm in an individual patient eg associated aneurysms 2 the classification does not recognize that an avm with high-grade risk for surgery is not necessarily dangerous to the patient and 3 the classification.
Its utility is based on accurate initial diagnosis that correlates consistently with clinical presentation disease course and treatment. And Interventional Radiology 28730All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi India. Spetzler-Martin classification of cerebral AVM at 4D contrast-enhanced MR angiography and at DSA matched in 18 of 18 patients for both readers which yielded 100 interobserver agreement K 1.
They can be congenital or acquired ref. Up to 65 of pulmonary AVMs are found in the lower lobes of the lung. Cirsoid AVMs have multiple dilated vessels with a corkscrew appearance resembling varicose veins with interconnecting fistula.
Venous malformations vms are the most common vascular malformation accounting for 4464 of all vascular malformations. There is direct arteriovenous communication with no intervening capillary bed. It correlates with the risk of neurologic deficit after surgical resection of the AVM.
AVMs can have one or multiple feeding artery. As information has been gleaned a new classification system has emerged that divides vascular anomalies into neoplasms and malformations. 34 vms consist of small or.
Brain arteriovenous malformations AVMs are abnormal vascular connections within the brain that are presumably congenital in nature. The classification of vascular anomalies and their main clinical and MR imaging features are summarized in Table 1. Arteriovenous malformations AVMs are characterized by an abnormal leash of vessels allowing for arteriovenous shunting.
A brain AVM may also be a part of more extensive disease eg cerebrofacial arteriovenous. Renal arteriovenous AV shunt a rare pathologic condition is divided into two categories traumatic and nontraumatic and can cause massive hematuria retroperitoneal hemorrhage pain and high-output heart failure. Classification The Spetzler-Martin grading system for AVMs introduced more than 30 years ago classifies AVMs on a 5-point scale based on the size of the nidus location in eloquent or noneloquent regions of the brain and the pattern of venous drainage.
Stages 2 and 3 are intermediate with stage 3 lesions demonstrating ulceration bleeding pain and necrosis. It is helpful to compartmentalize AVM angioarchitecture into three components. There is currently promising research in the identification of genetic markers and molecular targets but there is no recognized pharmacologic treatment for AVM available yet.
Myelopathy from venous congestionhypertension. Table 1 Clinical and MR Imaging Features of Vascular Anomalies SE spin-echo SI signal intensity T1WI T1-weighted images T2WI T2-weighted images. The Schobinger classification is a clinical assessment of vascular shunting that is predictive of treatment success Table 2.
1 Pulmonary AVMs may be classified as simple with a single feeding and draining vessel 80 of cases or complex with 2 or more feeding or draining vessels 20 of cases. We describe the various classification systems which have been devised to define the multiple entities included under. Each of these components have certain features which can either change natural history affect clinical management or influence the clinical presentation.
Intramedullary glomus AVM type.

Pin By Marek Tupy On Education Ultrasound Physics Radiology Imaging Mri Brain

Cerebral Pial Arteriovenous Malformation Avm

Pericallosal Lipoma Tubulonodular Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org Radiology Radiology Imaging Brain Images

Racing Car Sign Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org Radiology Brain Images Medical Imaging

The Borden Classification Of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Davf Groups These Lesions Into Three Types Based Upon The Site Of Ve Borden Classification Proposal

Pulmonary Avm Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org Pulmonary Radiology Vascular

Endovascular Treatment Of Arteriovenous Malformations Of The Head And Neck Focus On The Yakes Classification And Outcomes Journal Of Vascular And Interventional Radiology

Choledochal Cyst Cysts Type I Development

Spectrum Of Imaging Manifestations Of Vascular Malformations And Tumors Beyond Childhood Radiologic Clinics

What Are Vascular Anomalies Ucsf Radiology
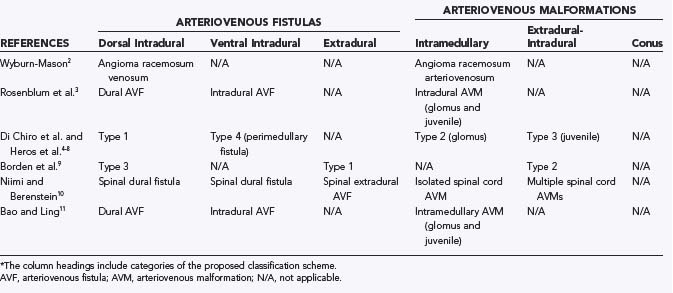
Classification Of Spinal Arteriovenous Lesions Neupsy Key

Vascular Malformation Classification References T M O Couto Download Scientific Diagram

Vascular Malformation Classification References T M O Couto Download Scientific Diagram

Yakes Avm Classification System 8 Download Table

Issva Classification Of Vascular Anomalies A Simple Grepmed

Amar Udare Md Radiogyan Com On Twitter Excellent Talk By Dshatzkes On Vascular Malformation At The Theapdr Noon Conference Take Home Point Be Careful Of What You Call A Hemangioma Refer
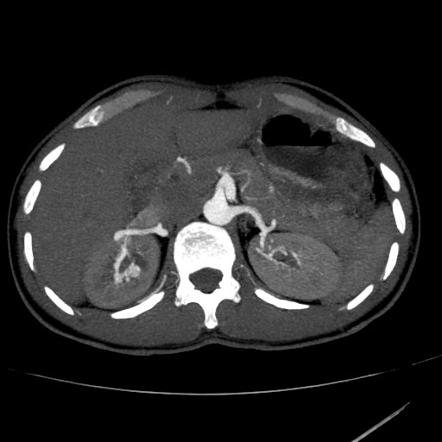
Renal Arteriovenous Malformation Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org


Comments
Post a Comment